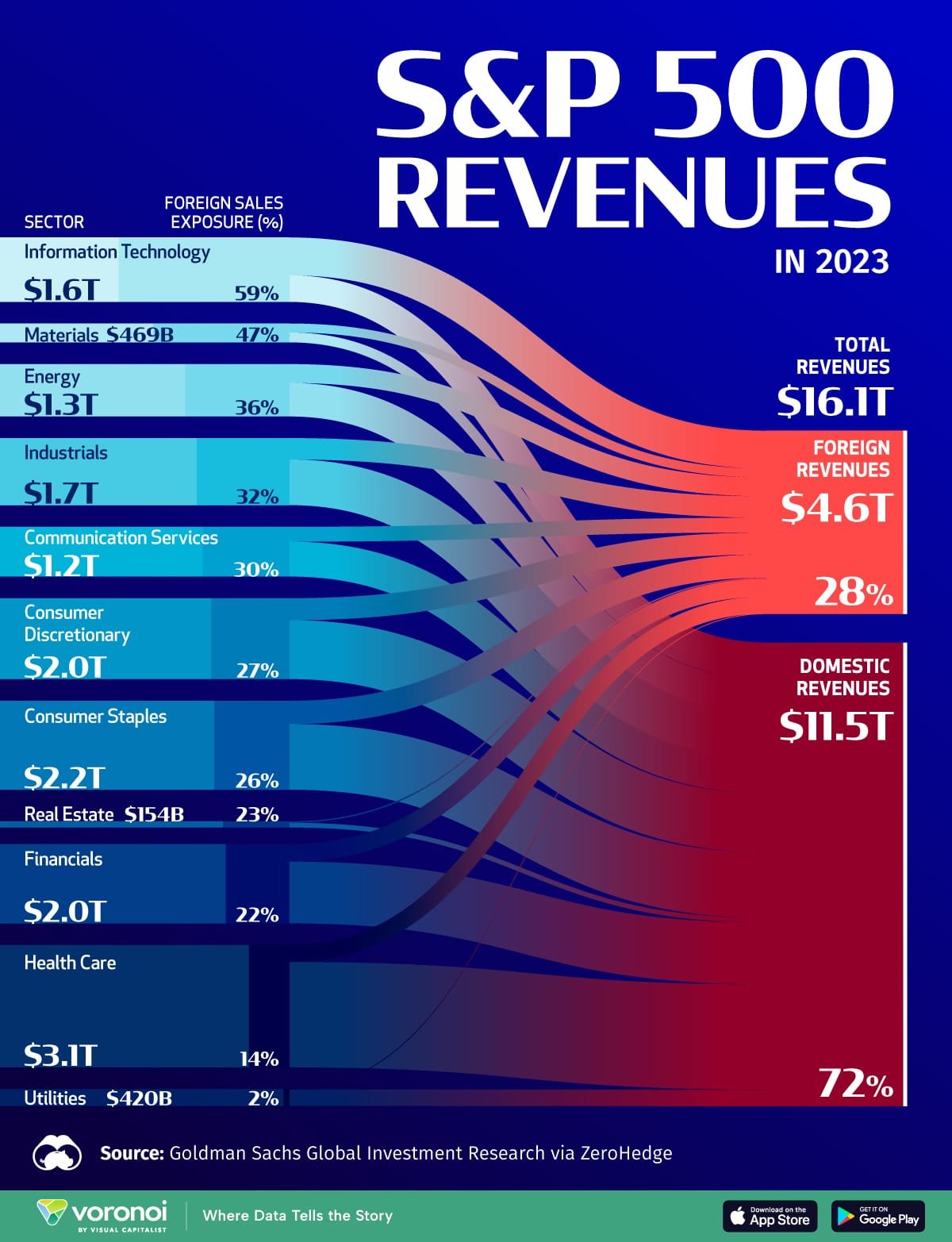
The State Bank of India (SBI) generates revenue through various income streams, primarily from interest-based income and fee-based income. Here’s a breakdown:
| Income Stream | Description | Percentage of Total Income |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Income | SBI’s main revenue source is the interest charged on loans given to individuals, businesses, and governments. | 60% |
| Investment Income | SBI invests in government bonds, securities, and other financial instruments, earning from interest and capital appreciation. | 15% |
| Fee and Commission Income | SBI charges fees for various banking services such as fund transfers, loan processing, insurance distribution, and advisory services. | 10% |
| Trading Income | Income from the trading of foreign exchange, derivatives, and other financial products. | 5% |
| Miscellaneous Income | Includes income from other activities like penalties, service charges, and rental income from SBI’s properties. | 10% |
SBI’s primary income comes from interest on loans and investments, which makes up approximately 75% of total income. Fee-based services help diversify its income sources, providing stable revenue during low loan demand periods. This income distribution showcases how SBI maintains profitability through a mix of interest-earning assets and diversified services.